This Hot Wheels car is a diecast model without any steering system or engine. Therefore, we need to manually design and add all of these components to convert it into a Bluetooth-controlled car.
Step 1: Build the Engine
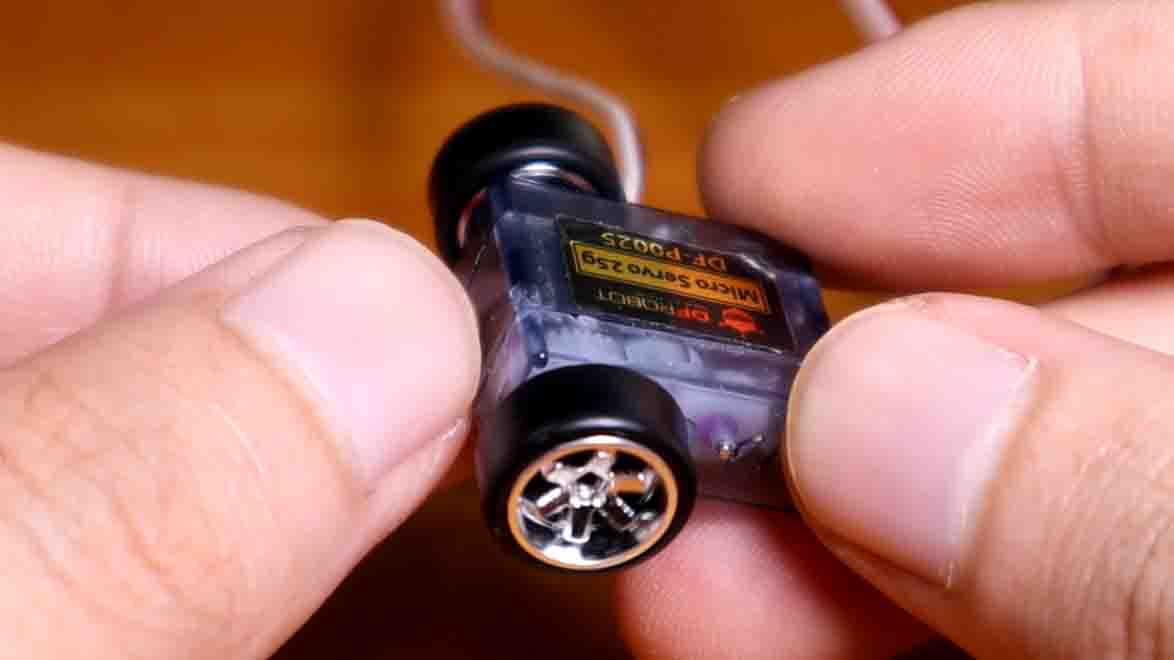
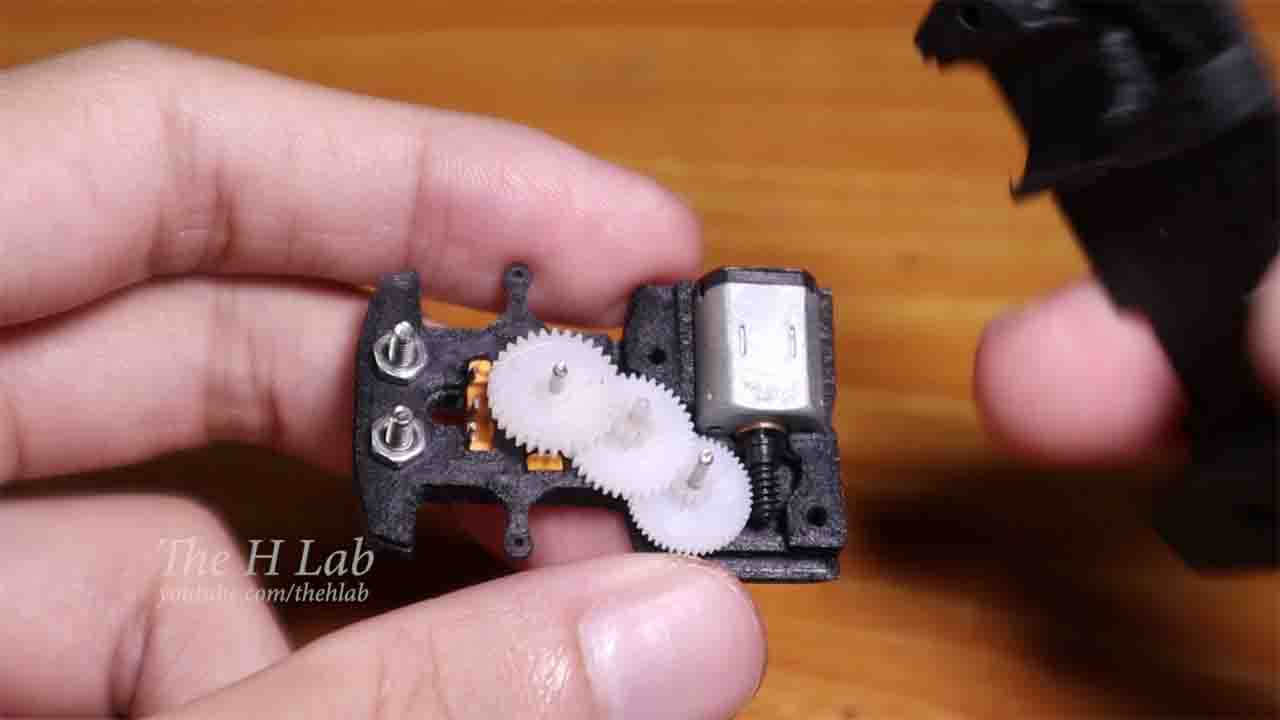
We will use a 3.7g servo to create the engine. This servo is a gift from DFRobot and can be purchased from their website.
Step 2: Design the Steering System
We will also use a servo to create the steering system. This time, we will use a 9g servo. A worm gear will be used to make the steering system small enough to fit in a 1:64 scale. The worm gear can be obtained from an old compact camera.
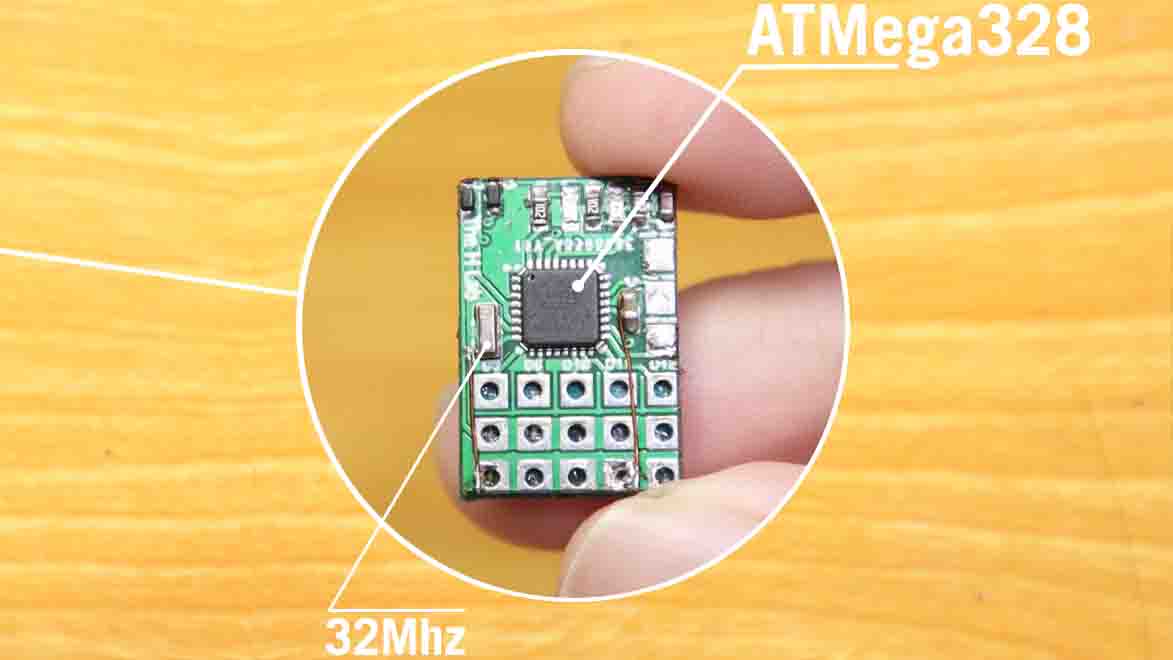
Step 3: Add the Bluetooth Receiver
We will use a tiny Bluetooth receiver board designed by The H Lab team to receive control signals from smartphones. This receiver is actually an Arduino Nano board connected to a JDY-10. The JDY-10 is a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) breakout board.
To make the receiver small enough to fit into any tiny remote-controlled toy, we designed a custom version of the Arduino Nano with only the necessary elements and input/output pins, which will be used to control the servos. We then laid out the I/O pins in the same way as any popular RF receiver.
Step 4: Add the Frame
The final step is to add a frame to hold all of the components. The frame is a product of 3D printing technology and was designed using Blender.
Once the frame is in place, we can wire and solder everything together. And that's it! We now have a tiny Hot Wheels car that can be controlled by a smartphone.